Because you have two eyes, everything we see is a combination of two images fused together by your brain. Each eye captures a clear photo like a camera and your brain combines the photos making one single image. This line of communication takes place constantly when your eyes are open. When your eyes and brain are aligned, this happens seamlessly. When the eyes are out of sync, or misaligned, it puts higher demand on the visual system which must work constantly to compensate for the misalignment.
While each eye may capture a clear photo individually, if there is a misalignment between your eyes, the brain is forced to manually combine every pair of photos. This constant adjustment continuously stimulates the trigeminal nerve.
Overstimulation of the trigeminal nerve—the largest and most complex nerve connected to the brain, and the one responsible for sending sensations to the head, eyes and shoulders—results in visually induced Trigeminal Dysphoria.
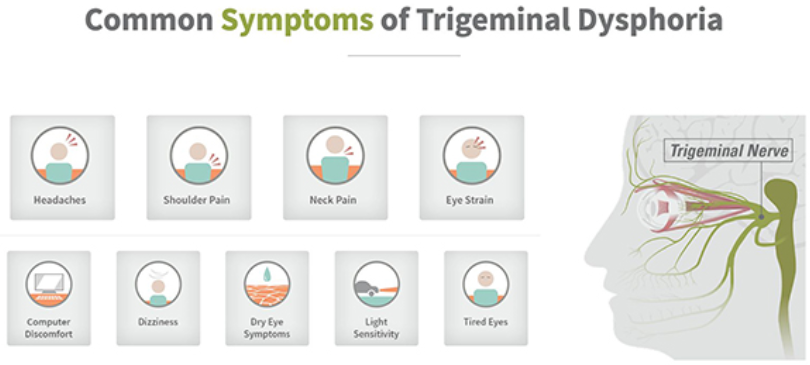
To reduce the symptoms of eyestrain, headaches, blurred vision, dry eyes, neck and shoulder pain, schedule an eye exam and discuss your options with your doctor. Harvard Eye Associates now has specialized testing for measuring the degree of misalignment of your eyes at distance and near.
A Three-Minute Test Can Change Your Life! The neurolens® measurement test is performed in less than 3 minutes during your regular eye exam. The test measures the degree of your misalignment at distance and near. Neurolenses® are specialty prescription lenses that add a contoured prism to bring your eyes into alignment, relieving the headaches, neck/shoulder pain and eyestrain often caused by using digital devices, reading or doing detail work. The test results will guide your doctor in determining if you have a misalignment in your vision and the contoured prism prescription that is right for you.
Click here to watch a video that will explain more about how neurolenses can help relieve the symptoms of eye misalignment and trigeminal dysphoria.








