Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Most people are aware that diabetes is a disease of blood sugar levels but it is actually a disease that affects blood vessels –primarily the small capillaries. The only place in the body we can directly see these capillaries is in the eye. When the blood vessels in the retinas are affected, this is called diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness in American adults. It is estimated that 45% of diabetic Americans have some form of the disease. The main concern with diabetic retinopathy is that it can be without symptoms until it is very advanced when permanent, irreversible damage has been done. Regular retina screenings and eye exams help to diagnose changes earlier when treatments can help prevent vision loss.
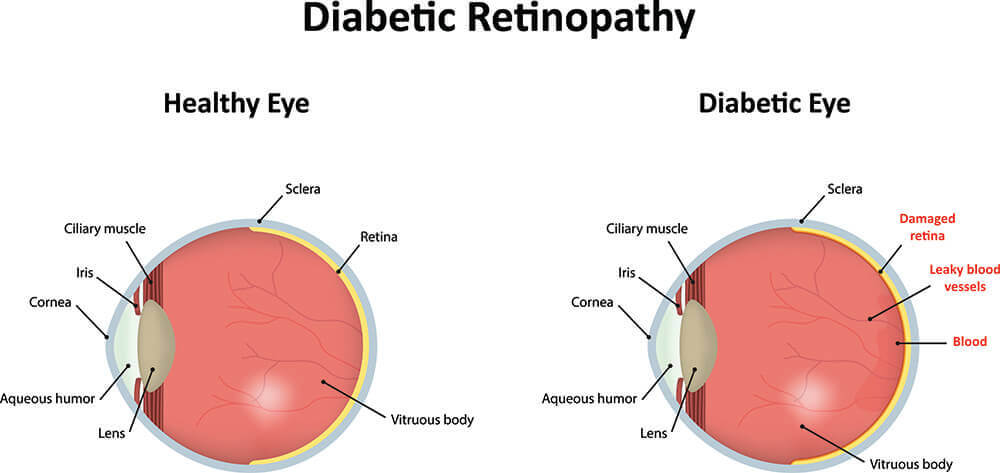
When diabetes affects the retina, there can be bleeding and leaking of fluid which may or may not affect vision and require treatment. In severe cases, the blood vessels and retina can become so damaged that they stop delivering blood to the retinal cells and even cause the growth of abnormal vessels. This is a very advanced stage and usually requires medical and/or surgical treatment.
Approximately 30% of diabetics with retinopathy have blood vessels that leak fluid into the central retina. This is called diabetic macular edema (DME) and is the leading cause of vision loss in diabetics. This condition often requires careful monitoring and treatment. If severe enough, treatment starts with medication injections into the eye and/or retinal laser which oftentimes helps to reduce the fluid and improve vision.
To decrease the risk of developing severe diabetic retinopathy or diabetic macular edema, it is important to work with your medical team to control blood sugar levels, monitor your hemoglobin A1c (a blood test performed by your diabetes doctor), blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy usually occurs in both eyes but often has no early warning signs or symptoms until there is advanced disease. It is recommended that diabetic patients get dilated eye exams at least once a year to identify the early signs of the conditions.
In more advanced stages you may experience:
- Cloudy or blurry vision
- Loss of central or peripheral vision
- Patches of blurry vision
- “Blood” or red spots in your vision
- Tiny dark spots or “cobwebs” floating in your vision
- Complete vision loss
If you are diabetic and notice any change in your vision, see your eye doctor immediately to check for diabetic eye disease.
Reducing Your Risk
- Keep blood sugar under strict control
- Monitor blood pressure
- Maintain healthy cholesterol levels
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get an eye exam at least once a year
- If pregnant and diabetic, have a dilated eye exam each trimester
Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy in Orange County, CA
Treatments are very effective in reducing vision loss from this disease. In fact, even people with advanced retinopathy have approximately a 90% chance of keeping their vision if they get treatment before the retina is severely damaged.
Usually, there is no treatment for the early stages of diabetic retinopathy unless macular edema or severe hemorrhage is detected.
- Intraocular injections: Medication injections with steroids or medications called anti-VEGF can be given into the eye to help reduce macular edema, reduce abnormal blood vessels, or to prepare the eye for retina surgery.
- Focal laser treatment: During this procedure, a focused laser directly targets the damaged blood vessels. It seals the vessels and helps to stop them from leaking. Often this is used in conjunction with intraocular injections and sometimes more than one treatment may be needed.
- Panretinal laser treatments: If there are significant vessel damage and growth of abnormal vessels, this laser treatment is performed to get the blood vessels to shrink and reduce the risk of vision loss, bleeding, diabetic glaucoma, and diabetic retinal detachments. Peripheral vision and dim light vision can be reduced with this treatment, in order to save the remaining central sight and may need repeating if new blood vessels appear.
- Vitrectomy surgery: This surgery is performed by a retina surgeon to remove blood or other material that has leaked into the vitreous. At the same time, the surgeon may also need to remove any significant scar tissue and/or perform a retinal laser. This is typically performed as an outpatient surgery.
If you are diabetic, you need to have a dilated eye exam at least once a year with one of our Orange County diabetic retinopathy specialists. Contact us today to schedule your exam.










